Smart Energy Meter Surveillance Using IoT
Smart Energy Meter have received quite a lot of acclaim across the globe in recent years. Industries are realizing the benefits of smart meters and assuming them to improve the efficiency and accuracy of utility management.
There are near about 13.8 million smart and advanced meters that are operating across homes and businesses in Great Britain, by large as well as small energy suppliers. That means 8% increase in operating meters from the previous quarter. Asian countries are placing themselves as the leaders in this space: they have a goal that by 2022, 70% of all homes in the region will be connected via smart meters.
Organizations have already stated investments of more than USD 62 billion for smart meter infrastructure. Traditional meters which were earlier used, measures only total consumption, whereas smart meter is an internet capable device that is able to report when and how much of resources such as water, energy and natural gas are consumed.
Utility industries can use smart meters to decrease their operational costs greatly. Smart metering benefits by eliminating the hassle of monthly or quarterly meter readings. In the past, to make it simple for users to take readings, meters have been located outside of buildings or at the edge of gardens.
Smart meters can, however, be located anywhere in the household. Thanks to smart meters, using real-time dashboards, homeowners and renters can keep a closer eye on their energy consumption. And most important the insights provided by smart meter infrastructure can be also used for the formation of an even more customer-centric structure.
With IoT solutions for smart meter, you can support to improve customer service through actionable insights generated from meter data.
Smart Meters:
Smart meters are new kind of gas and electricity meters and offer a wide range of smart functions. Smart metering will help utilities by enhancing customer satisfaction with quick interaction, while giving consumers more control of energy utilization to save money and minimize carbon emissions.
All domestic customers will be provided with an In-Home Display (IHD) as part of the smart meter turn-out, which shows how much energy is being utilized and how much it is costing in real-time. This gathered information will help them to monitor and manage their energy utilization, save money and minimize emissions. Smart meters will also show end to end evaluated meter readings, providing customers with more exact bills.

It has functionality that allows carrying meter readings to energy suppliers and collecting information remotely. Each large energy supplier describes the number of smart meters it has located and is operating in smart mode to BEIS (Department of Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy) on a quarterly basis, whereas small suppliers report to BEIS on an annual basis. BEIS maintains 75% smart meter coverage of 2020 target.
This involves both meters that are SMETS (Smart Metering Equipment Technical Specification) adaptable and those they suppose to upgrade to become SMETS adaptable. Some smart meters recently installed will require receiving updates before they are fully SMETS compliant.
Smart-Type Meters:
Most of the suppliers have preferred to make an early start by turn out smart-type meters without the full functionalities included in SMETS. These meters are installed in domestic sites that will require to be replaced with SMETS compliant smart meters by the end of 2020.
Advanced Meters (only installed in smaller non-domestic sites):
Advanced meters must be capable to reserve half-hourly electricity and hourly gas data, to which the customer can have timely access and the supplier has remote access. Advance Metering Infrastructure is a fused system of smart meters, communication networks and data management that allows two way communication between customers and utilities.
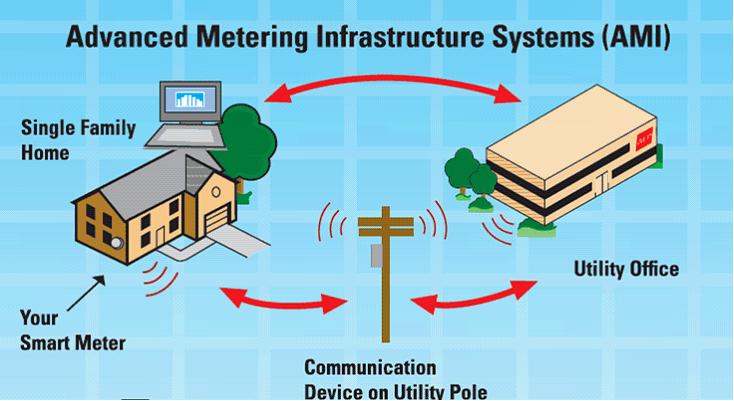
Traditional Meters:
Traditional meters are now days found in most domestic and smaller non-domestic sites (shops, offices, small hotels etc.) and do not have any smart ability. Traditional meters will be replaced by smart and advanced meters during the smart meter turn-out. Traditional meters include smart meters that are operating in traditional mode.
How IoT will change smart meters for utilities:
The concept of smart meters that are utilized to measure total gas and electricity usage predated the IoT. IoT is a simply the networking of physical devices which allows them to interchange data then energy & utilities companies building smart grids which includes a variety of operation and energy devices involving smart meters, smart appliances etc, could be recognized important characteristic of the advanced IoT development.
Most of the utility companies have already optimized such processes as prior to increasing interest and investments in IoT. So how do we see IoT effecting utilities companies and their smart meter advantages moving forward?
Reduce Energy consumption:
Most smart meter edge have centered around operational savings first and are now shifting into supplying customers with data and transparency on energy consumption. Combining smart meters with IoT transmutations in the home will maximize energy productivity.
For example, smart thermostats are becoming omnipresent but there is no constant IoT platform for connecting such an IoT device with smart meters.
Cognitive systems are the one that executes the cognitive work of knowing, understanding, designing, deciding, problem solving, monitoring, composing, estimating and judging. When this system is combined with open IoT platforms to achieve data, it could modify how consumers consume energy.
To use this data efficiently, the devices are connected safely to an IoT platform over the internet that gathers and monitors the data .Via a number of dashboards, users and energy suppliers can access this data. An added advantage is that this could help support grids for maximum use and provide more reliable service.
Enable renewable energy and micro-grids:
Consumer demand for renewable energy is at a higher level, as showed by rapid growth and revolution in solar rooftop technology and adoption.
Smart meters, feeding into smart grids, will enable utilities companies to better control bi-directional power flows into and out of their grids and give customers the insights required to learn their own energy infrastructure investments. But more significantly, smart grids will enable larger-scale renewable projects conducted by utilities companies.
But controlling this data is hard, especially when utilities attempt to supply customers with individual grid management.
This is where cognitive solutions can help smart grids. Cognitive solutions can help make best decision by recognizing grid conditions in real-time via the IoT and then can give each client the entire customization they’re looking for to drive renewal acquisition.
Especially in emerging markets of Asia and Africa, the smart meter infrastructure can be held back by the scarcity of general high quality electric and telecoms network connectivity. For example, it is difficult to hold power line communications technology on the smart electric network, which is generally used in Europe. In the same way using wired telephone lines to move smart meter data can be difficult as well. To connect the smart meters to the IoT platform that they rely on to function, they need a strong connection that is not always available. In many cases, measurement stations are located behind thick walls which can cause difficulty for conventional mobile networks.
A Long Range Wide Area Network ( LoRaWAN) can be the solution to these problems which is specifically designed for IoT devices such as smart meters. It’s an inventive networking solution that uses a number of various frequencies in the ISM-band depending on region. This network technology only supports a particular data bandwidth per device, but it is remarkably more energy systematic and definitive. Smart meters for gas utilization can be installed independent from the main power source with a battery life of up to 15 years with the help of low power consumption feature of LoRaWAN.
LoRaWAN’s range (of between 4 and 20 km) is another significant advantage in building the infrastructure for smart meters.
One of the biggest LoRaWANs of this kind is currently being built by Tata Communications in India. Over an open IoT platform, such a large network can be used for a number of other IoT applications away from smart meters, including the way and acting as the critical infrastructure for smart cities and communities.
Edge analytics will make meters truly smart:
This year IBM and Cisco reported a partnership on edge analytics and while this has clear applications for utilities companies controlling complex and geographically distributed infrastructure, edge analytics might also help enhance the intelligence of smart meters.
Using edge analytics to set cognitive abilities into meters, their power and usefulness could enhance massively. This generally needs infrastructure investments by utilities around connectivity, but this could be more cost-effective than upgrading physical infrastructure and would also give considerable operational savings in addition to isolated and customized customer experience.
Connectivity everywhere-exceeding the internet
Using IoT platform
The important building block for a meaningful smart meter infrastructure is the IoT platform. Data is gathered via a smart meter and transferred over LoRaWAN, but only at the IoT platform level does the meter truly become smart.
IoT platform forms the core of the system. The data collected by the individual measuring devices has to be combined, stored and monitored. Here the whole system shows what specifically it can do. Such a platform requires to be accessible, strong, have good analytical abilities and, above all, ensure the security of any sensitive customer data.
Below are a few of the advantages of investing in an end-to-end IoT solution for Metering:
Gain valuable insight into the grid
Smart meters give a safe and secure source for real-time data on energy consumption and power supply quality. Enhance forecasting and efficient power-consumption.
Minimize cost of ownership
Operational and maintenance costs are reduced with remote monitoring of data and upgrades for large numbers of geographically scattered meters. Reduce operating expenses by managing manual operations remotely.
Easily comply with regulations
Automatic meter reading (AMR) via smart meters makes it easier to cohere to regulations and legal requirements.
Increase operational efficiency
Control asset utilization, notice malfunctions and leakages and take measures to protect any electrical failure based on data from IoT devices.
Manage demand and generation
Production capacity can be controlled depends on real-time data on energy consumption and power supply quality.
Secure the grid and prevent fraud
A safely encrypted solution prevents the grid from digital threats and helps protect energy theft.
Limited Data Consumption
Data on consumption helps customers understand and plan energy utilization and enables suppliers to create incentive for limiting consumption.
Improve offerings and transform business models
Higher customer satisfaction is feasible with more customized services depends on real user data. It improves customer service through profiling and cleavage.
You can achieve this and more with an end-to-end Industrial IoT solution that can transform your business.